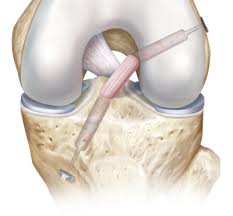
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) in the knee is used to stabilize and balance the femur and the tibia. The anterior cruciate ligament is at the center of the knee, forming an X- shape along with the posterior cruciate ligament.
Tearing of the ligament causes serious damage to the knee, which usually does not allow athletes to return to normal activity. If the rupture is not treated, knee subluxations can cause damage to additional parts of the knee such as cartilage or meniscus, and eventually accelerate the appearance of degenerative changes- arthritis of the knee.
Any rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament requires activation and restoration of the knee. The structure of the knee and the joint fluid do not allow the anterior cruciate ligament to regenerate and re-attach itself, and the persons affected need to change their activity habits or seriously consider surgery to reconstruct the anterior cruciate ligament.