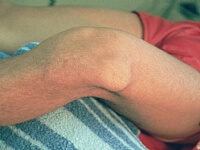
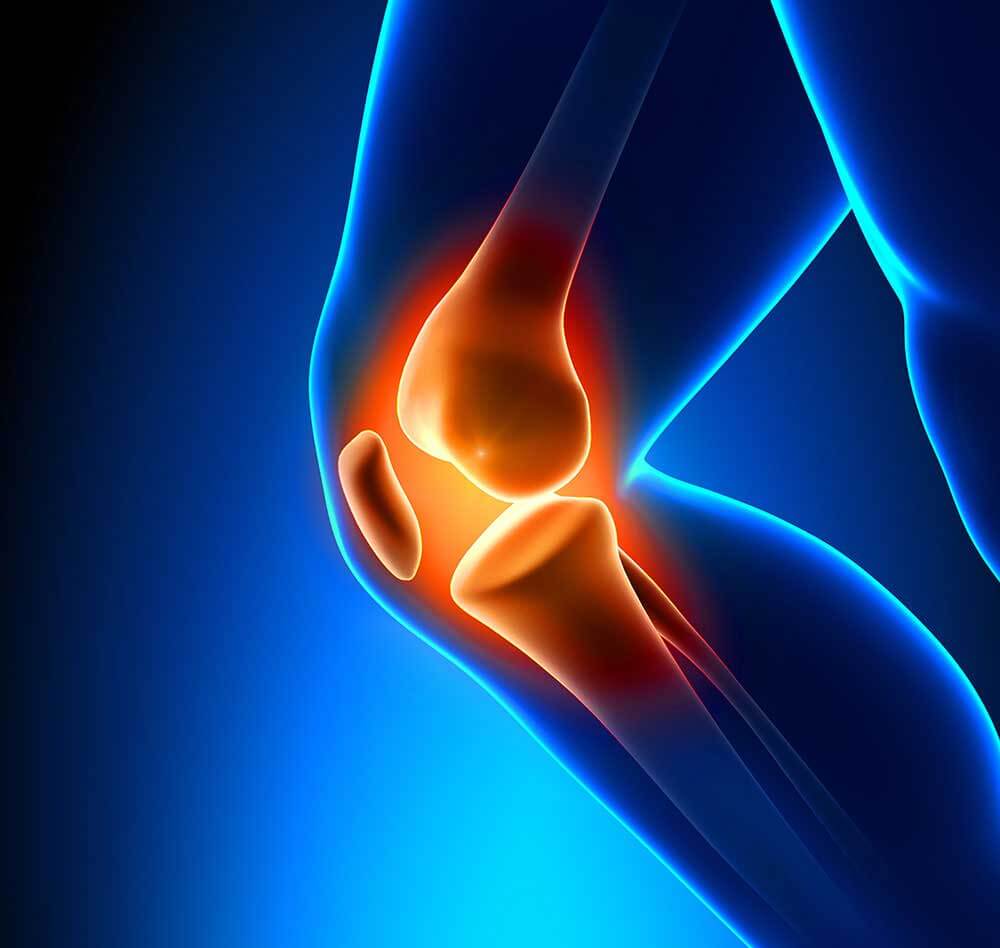
Patella dislocation occurs almost always in young people. This causes considerable pain in the knee, and it affects the patient’s ability to live an active life. Knee cap dislcation may cause damage to the cartilage of the knee, which causes the appearance of free bodies in the knee, or to a rupture of meniscus in the knee.
The main reasons that precipitate patellar dislocation are:
- An abnormal anatomical structure that allows the patella to exit from the knee.
- Over-flexibility of the joints.
- Moderate trauma, causing a rupture of the ligament, which connects the inner side of the patella to the inner side of the knee